

Flowers have always been associated with beauty and poetic elements, but digging deeper into their anatomy reveals their importance associated with other parts of the plant.
There are several different types of flowers that have been identified today, but there are some parts that are found to be common in all flowers.
Plants are usually classified based on their ability to produce a flower. On this basis, plants are classified into two categories that are:

Here we have discussed the different parts of a flower that collectively constitutes the anatomy of the flower.
The main parts of a flower include
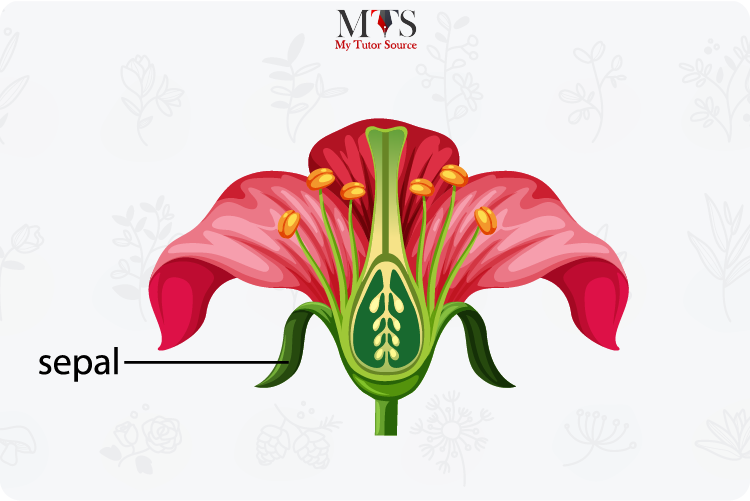
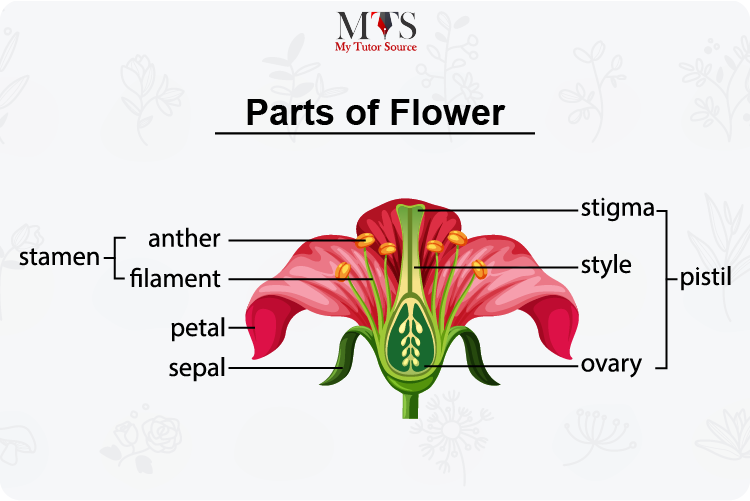
The sepal of a flower is usually green and resembles a leaf-like structure. The primary function of a sepal is to protect the bud as it emerges to form a flower. The sepal encloses the bud in its embrace when it is immature and growing to become a flower. This embrace proves to be a protective mechanism that allows the bud to bloom properly into a flower.
The sepal remains closed when the bud is in its immature form, but as soon as the bud grows to form a flower, the sepal opens up to provide structural support to the newly formed flower.
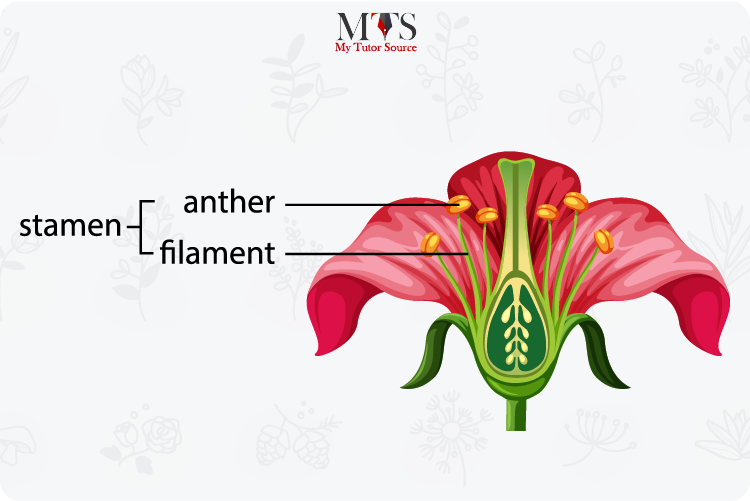
Collectively known as the stamens, this part of the flower is usually responsible for the reproduction process in the plant. Being a reproductive organ, the stamen is composed chiefly of a linear stalk-like part known as a filament that is connected to the end with the upper part of the stamen that is known as the anther. These two parts of a stamen work together to produce the pollen. The stamen as a whole is connected to the base of a flower.
Stamen is more commonly referred to as the male reproductive organ of a flower as it gives rise to the male reproductive cells in the form of the production of pollen grains.
The filament of a stamen is responsible for keeping it in a high position and near to the pistil where it transfers the pollen grain to the female reproductive organs for the further process of reproduction. The pollen produced is then made available to the pollinators who further use it for reproduction.
Some flowers have just a few stamens on them while some have too many, based on the type of flower.
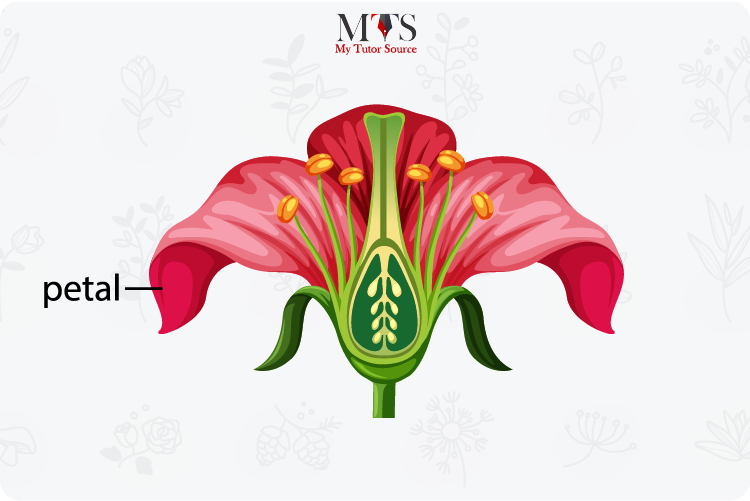
Petals are the part of a flower that is often highly pigmented with brighter colors and often with a great smell. These prominent features of a petal do not only make a flower more beautiful but it has a useful purpose as well.
The scent and the pretty colors of petals are used to attract the pollinators towards the flowers. In the collective form, the petals of flowers are known as the corolla.
The formation and placement of petals vary from flower to flower. Some flowers have layers of petals on them making them a full bulky flower whereas others do not have many layers, just a few petals on them.
Other than attracting pollinators, the petals are also responsible for the protection of reproductive organs enclosed within the petals.

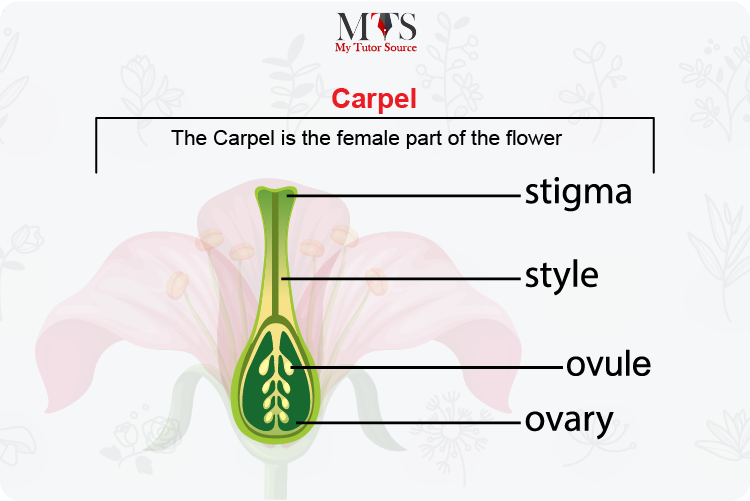
The carpel is the female reproductive organ of a flower. A carpel is also sometimes called the pistil of a flower. The carpel holds a sac-like structure in the middle that is known as the ovary. The ovary is responsible for the production of ovules that are the female reproductive cells.
Furthermore, the carpel extends towards the elongated tube called the style which leads up to the sticky part that is known as the stigma. Stigma is the part where the pollen grains land from other flowers that come from either a source of wind or through pollinators. The sticky surface is an ideal texture to capture and utilize the pollen grains for reproduction.
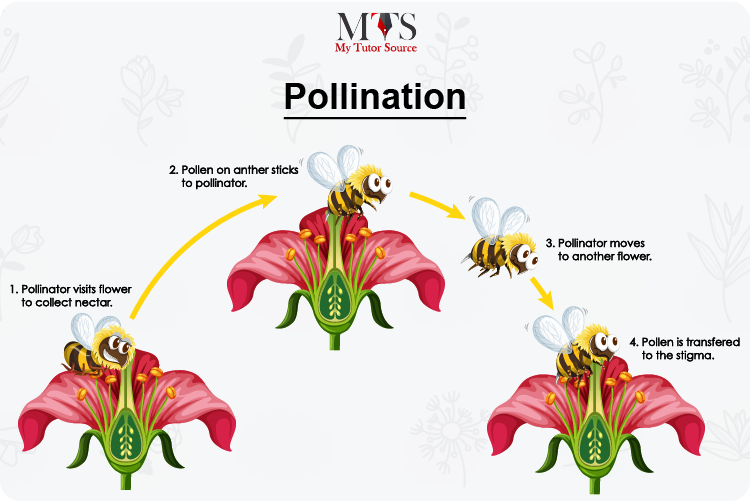
Usually, when the anther produces the male reproductive cells or gametes, they are then transferred to another flower either by the wind or some insect, like bees or flies. The insects are referred to as pollinators. The pollinators pick up the gametes from the anther of one flower and take them to the stigma of another.
The stigma then passes down the gamete to the lower part of the carpel where lies the ovary. In this way, the gametes of one flower reach the ovules of the other flower, making it possible for fertilization to occur. This whole process is generally referred to as pollination.
When an ovule has been fertilized by a gamete, the ovary then swells up. The swollen ovary allows the fertilized ovule to be protected in that covering. Once the reproductive process is done, the ovule turns into a seed of a whole different fruit that can be sown from the flower.
Pollination makes it possible for the plants to further reproduce and extend the species. Other than this, pollination also makes many flowers and eatables available for human consumption. For the better survival of the ecosystem, the process of pollination must keep on occurring as it does.
There are some other parts of the flower that are not as highly important as the ones mentioned above, yet they remain relevant to the anatomy of the flower.
Here are some of the other relevant terms associated with flower
This is the sticky part on top of the female reproductive organ that is the carpel. This is where male reproductive cells from another flower are transported to.
This is the tube through which the stigma and the ovary remain connected. This tube becomes the mode of transferring the gametes collected on the stigma to the ovary below for fertilization.
This is the female reproductive part of the flower where ovules develop. These ovules then become seeds once they are fertilized by the gametes that come to the ovary via the style.
These are the female reproductive cells that are produced by the ovary and stay there to be fertilized by the gametes that land on the stigma.
The filament is the linear tube-like structure that is connected to the anther. This part aids in the production of pollen grains in the flower.
The upper end of the stamen that is connected to the base via the filament is known as the anther that aids in the production of pollen grains.
Pollen is the male reproductive cell that is fertilized by the ovules by transfer from one flower to another.
The carrier that usually transfers pollen from one flower to another is known as a pollinator. This could be wind or some insects like bees.
All the different parts of a flower serve an individual purpose. Even the color and fragrance of flowers help it to attract pollinators so that fertilization and pollination can occur. Do you wish to learn more about the anatomical features of a flower and other plants? Learn all about it from our private tutors who offer professional guidance to students.