
The cell is not only the smallest unit supporting the life of living beings; it is also the most vital one. This life-providing unit contains many small components that work together to make the cell function properly. Cells are either prokaryotic or eukaryotic. As it has a defined nucleus body and a cell membrane surrounding all the cell components, the animal cell is considered eukaryotic.
Learn about it in detail from our private biology tutors.
A eukaryotic cell is known to have organelles that are membrane-bound. These mainly include the nucleus enclosed in a nuclear membrane, and a plasma membrane that encloses all of the organelles in the eukaryotic cell. Animals, plants, and human beings come under the category of organisms having DNA held within the eukaryotic cells in their body.
Here we have discussed the different functions of the components of animal cells. An animal cell is a eukaryotic cell with a membrane-bound nucleus, but unlike the plant cell, it doesn’t have a cell wall surrounding the organelles.
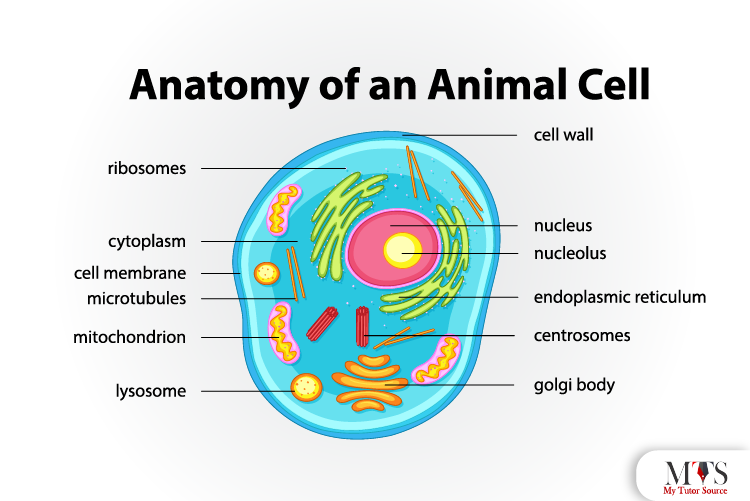
These are some of the main components of an animal cell that work together for the cell’s normal functioning.
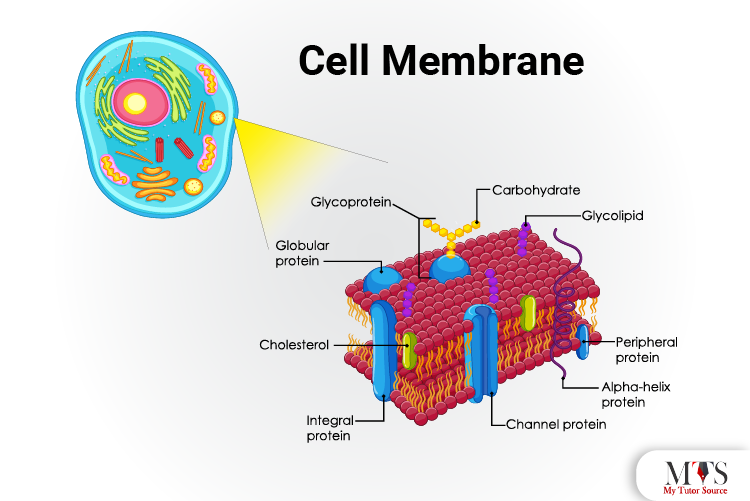
The cell membrane is also known as the plasma membrane. This membrane encloses and protects all the organelles present inside the cell by controlling what goes in and out.
The cell membrane is mainly composed of fats and proteins. The protein layer is embedded between the two layers of phospholipids. The protein layer between the bilayer ensures that no unwanted substances go in and out of the cell.
The lipid bilayer means the membrane has two layers of phospholipids. The inside of the lipid layers consists of hydrophobic phospholipids, whereas the outside layer consists of hydrophilic phospholipids.
The hydrophobic phospholipids limit the access of water-soluble molecules, and hydrophilic phospholipids allow the water-soluble contents to pass through. In this way, hydrophobic phospholipids become impermeable for the water-soluble compounds, and the hydrophilic phospholipids become permeable for water-soluble compounds.
These are some of the special functions of the cell membrane:
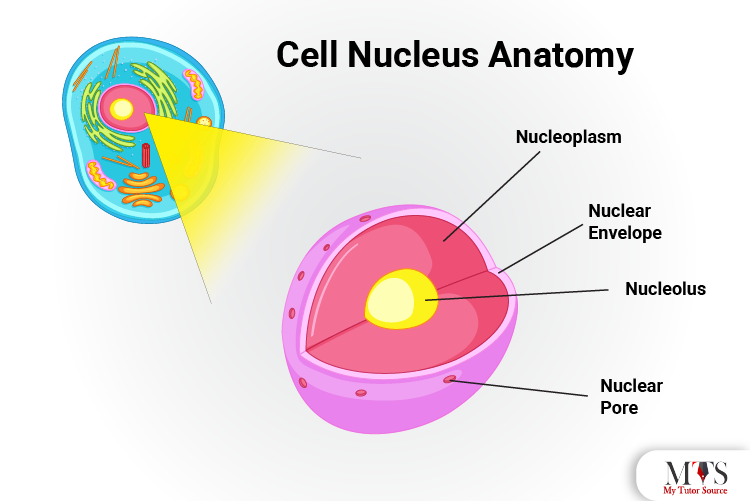
The nucleus is one of the main components in the animal cell as it contains genetic and hereditary material. The nucleus is responsible for the cell’s normal functioning as it regulates several activities associated with cell growth and survival.
The nucleus has further essential units, including:
Nuclear envelope: The nuclear envelope is the membrane that surrounds the components of the nucleus and keeps the other cell organelles separated from the cell nucleus.
Nucleoplasm: The nucleoplasm is the chemical protoplasm material in the nucleus that maintains and supports the structure of the nucleus.
Nucleolus: It is the spherical body in the nucleus associated with the synthesis of ribosomes that are further transported to the cell cytoplasm to produce proteins.
Functions of the nucleus include:
The cytoplasm is the semifluid thick material embedded inside the cell that fills the whole cell. It is mainly composed of three main components: water, salts, and proteins. The cytoplasm separates the membrane-bound organelles like the nucleus and mitochondria because of the membrane. Other organelles rest inside the cytoplasm of the cell.
These are some of the main functions of the cytoplasm.
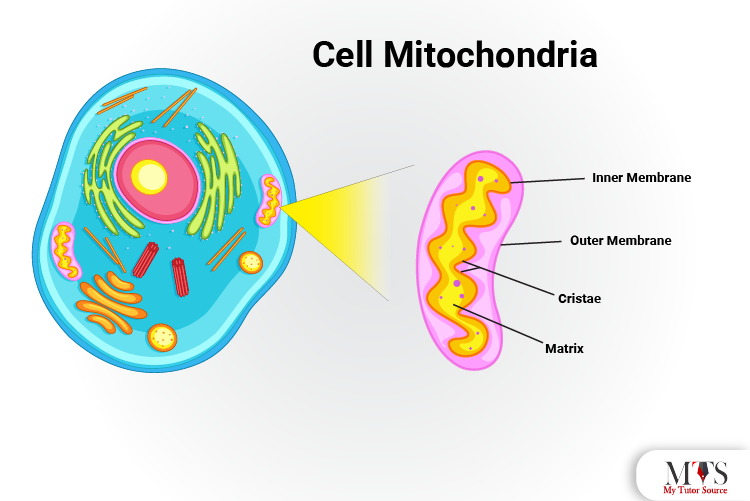
The cell needs the energy to perform its required functions. The mitochondria provide this energy. Mitochondria is more commonly known as the powerhouse of the cell. It generates the chemical energy to provide the cell with the power it needs in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
Like the nucleus, Mitochondria is also membrane-bound organelle separated from the cytoplasm by the membrane. Mitochondria has four main parts including:
-outer membrane
-Inner membrane
-Cristae
-Intermembrane space
These are the main functions associated with the mitochondria:
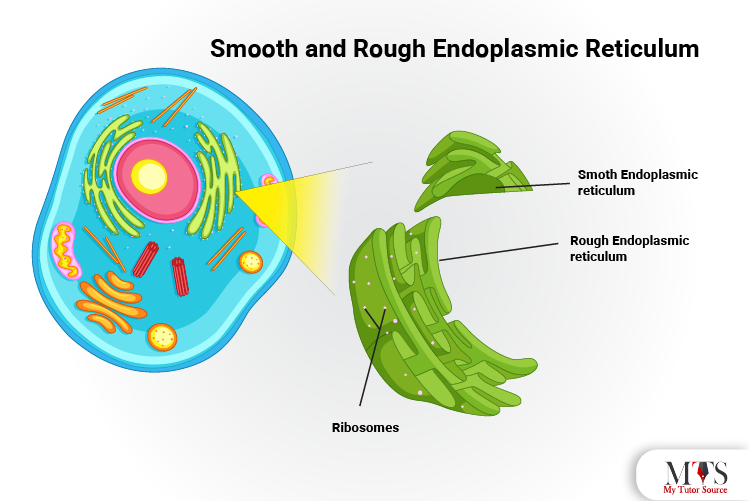
The endoplasmic reticulum is a tubular networking structure in the cell that provides the fundamental purpose of transportation and movement within the cell. The animal cell has two different types of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) that are
-Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER)
-Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER)
The smooth endoplasmic reticulum is involved in the synthesis of fat molecules. It is known as the smooth endoplasmic reticulum because it does not have any ribosome on its surface. Being granule-free, it has a smoother surface.
On the other hand, the rough endoplasmic reticulum is involved in the synthesis of proteins. It has granular molecules on its surface that are known as the ribosome. Having a granular surface, it is known as the rough endoplasmic reticulum.
These are some of the main functions of the endoplasmic reticulum:
In an animal cell, the vacuole is not as prominent as in the plant cell. It is a membrane-bound structure within the cell that is filled with fluid. It is responsible for the storage of water, nutrients, and waste from the cell.
These are the main functions of the vacuole in the animal cell:
Animals are organisms with multicellular structures inside their bodies. The group of cells in the body that work together to perform a particular task is known as tissue. Based on their functions and composition, there are several types of animal cells. A few have been discussed here, including:
Fat cells are also known as adipocytes or lipocytes, and collectively they make up the adipose tissue. The main function of fat cells is to store fat to further use it for energy processes. Fat in the adipose tissue is stored in the form of triglycerides, which are broken down by the cell enzymes to form fatty acids and glycerol. The components are then stored and utilized for the energy required processes.
Fat cells are found throughout the body, but the main locations include under the skin, around other organs like the heart, and between the muscles.
The storage by fat cells needs to be regulated, and if more than required fat is stored in the cells, then it can lead to other diseases, including diabetes, obesity, and cardiovascular disease.
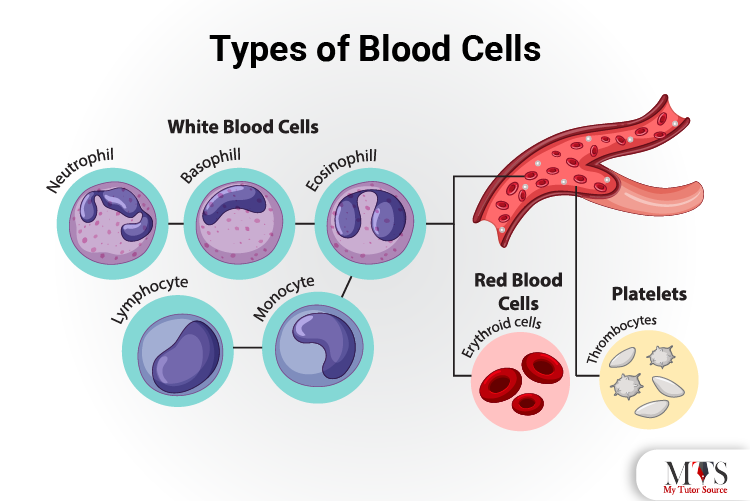
Blood cells, also known as hepatocytes, can be found through the blood in the body. The life cycle of a blood cell starts as a stem cell. It is not defined as any particular type of blood cell at this stage. As the stem cell matures, it is converted into a specific blood cell.
There are mainly three different types of cells found in the blood including:
-Thrombocytes (Platelets)
-Erythrocytes (red blood cells)
-leukocytes (white blood cells)
The platelets are irregularly shaped cells in the blood that originates as stem cell, and after maturing into the thrombocyte, they circulate in the blood for a time period of nine days. During their life cycle, they mainly provide the function of creating a blood clot where required.
Red blood cells are the most abundant type of circular cell present in the blood. The average lifespan of a red blood cell is 120 days. Its main function is to store hemoglobin to transport oxygen that facilitates respiration. Hemoglobin provides the red color of the red blood cells.
White blood cells are of several different types and shapes present in the blood. The life span of white blood cells is only 13 to 20 days, after which they are wasted from the body. All the different white blood cells are responsible for providing the body with the immunity it needs to stay healthy.
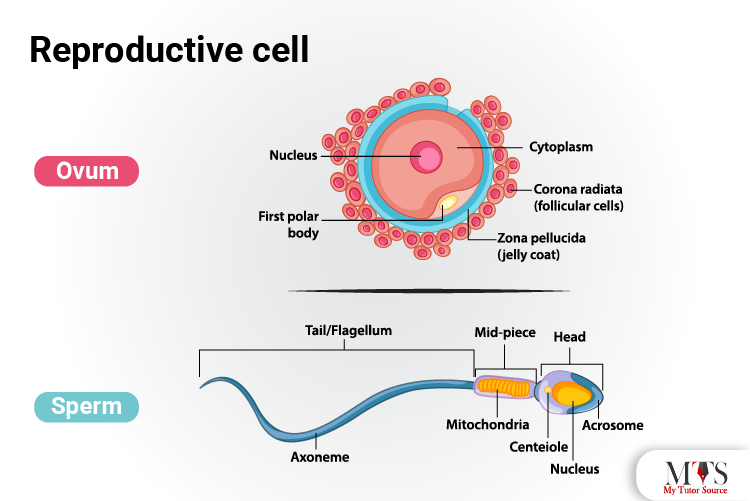
The reproductive cells in a body are known as gametes. The gametes in the male tissues are known as spermatozoa or sperms, whereas the gametes in the female tissue are known as ova or eggs.
These cells are responsible for the reproductive process in the body by the fusion of gametes and forming up a single cell that is known as a zygote. The gametes carry genetic information in the form of the chromosome. The chromosome from both gametes fuses to make up the resulting chromosome of the zygote.
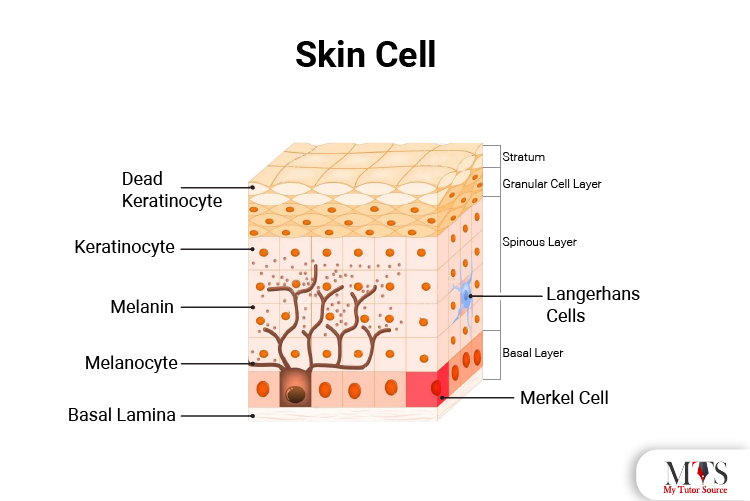
Skin provides a large barrier between the internal and external environment to the body in the form of skin. This skin is made up of several different types of cells, including keratinocytes, melanocytes, and Langerhans. The main function of the skin cells is to provide the body with insulation and a protective layer. The skin cells die, and the skin feels dry and flaky because of it, but eventually, the new skin cells are made.
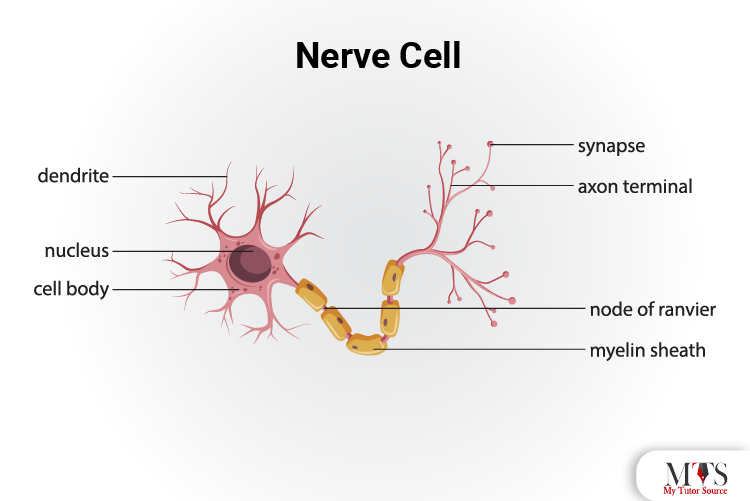
The nerve cells are also known as the neurons. They are the main components of the nervous system in the body of animals. They are responsible for receiving the signals from the stimuli that are the environment and then sending back a response to the muscles and organs for the responsive function.
There are three main parts of a nerve cell, including the stoma, axon, and dendrites.
The stoma is known as the cell body, the axon, the nerve fiber that originates from the stoma, whereas the dendrites are the branch-like structures that are responsible for transmitting the nerve signals.
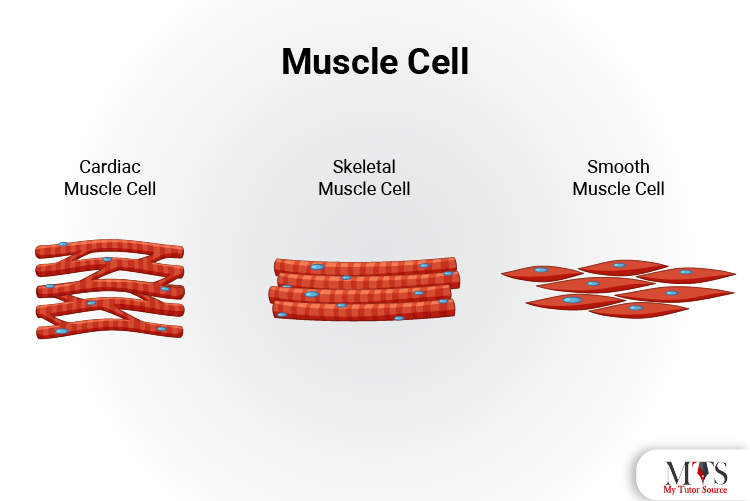
Muscle cells in the body are also known as myocytes. The myocytes collectively make up the muscle tissue. There are mainly three types of muscle cells that are found in the body, including the skeletal cells, muscle cells, and smooth cells,
Skeletal cells: the skeletal cells in the body are specialized elongated cells that are very flexible and provide the function of all types of movements in the body.
Smooth cells: The smooth cells make up the smooth muscle in the body, and it is responsible for the involuntary movement of muscles in the form of contractions.
Cardiac cells: the cardiac cells make up the myocardium tissue responsible for the heart’s normal functioning. These specialized cells act upon the impulse response from the nervous system and create rhythmic contractions that are more commonly known as the heartbeat.
The animal cell is a eukaryotic cell that contains many complex materials. These cell components are responsible for the normal functioning of the cell so that it would be able to provide the specific function expected of it. Based on the specialized functions of an animal cell, there are several different types of cells, as discussed above. These cells make up the tissues, which then make up an organ.
If you wish to learn the different areas of biology in detail, our private biology teachers make sure that you gain in-depth knowledge on your subject.